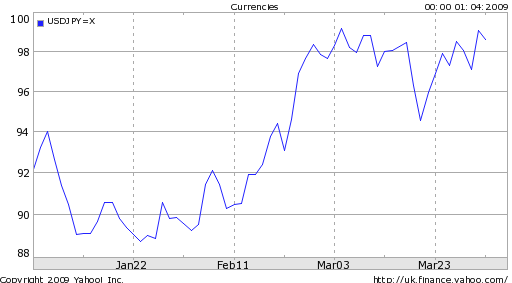
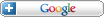
China’s Gold Holdings Surge 76% over Six Years
Based on the title, you’re probably groaning: ‘Wait, I thought this was supposed to be a forex blog?” Bear with me, however, as this subject is extremely pertinent to forex.
Last week, it was revealed that China has been clandestinely adding to its gold reserves since 2003, to the extent that its holdings increased by 76%, to approximately 1,050 tons. The news initially sent a ripple through forex and commodities markets, which were overwhelmed by the figures involved. After analysts had a chance to gather some perspective, however, the markets relaxed. You see, although the increase seems tremendous in size, it is quite small in relative terms.
It is relatively small compared to other countries: “This places China fifth in the world, ahead of Switzerland’s 1040 tons but behind the U.S. ranked first with 8,133 tons, followed by Germany (3,412 tons), France (2,508 tons) and Italy (2,451 tons).”
It is relatively small given the six-year duration of accumulation: “I think as soon as people realized it’s not a year-on-year increase, or a quarter-on-quarter increase, people realized it should not have that big an impact.”
It is small relative to China’s mammoth $2 Trillion forex reserves: “As a proportion of foreign exchange reserves, which have risen five-fold over the same period, gold now stands at a tiny 1.6 percent, versus 1.7 percent in 2003.”
On some level, the development has at least some symbolic importance, as it demonstrates that it cannot be taken for granted that China will simply continue to plow its (dwindling) trade surplus into Dollar-denominated securities, or even currencies in general. This is underscored by the suspicious timing of the announcement; China essentially waited six years before revealing its buildup in gold, probably in order to coincide with the uproar surrounding the Dollar’s role as global reserve currency. In other words, even though China’s gold purchases in and of themselves don’t amount to much, the Central Bank of China is trying to send a message that it will defend itself against “the depreciation risk of some foreign currencies.”
The announcement also explains the recent buoyancy of gold prices. Historically, there existed an inverse correlation between gold and the Dollar. This correlation has all but broken down as a result of the credit crisis, and for the first time a strong Dollar has been accompanied by high gold prices. Part of the reason may be increased buying activity by Central Banks, including the Bank of China: “The physical market remained well-bid by an unknown buyer despite bullion prices spiking to levels that normally cooled demand…Purchases were made in Shanghai, traders said, in an effort to absorb domestic production and lessen the impact of bullion prices on global markets.”


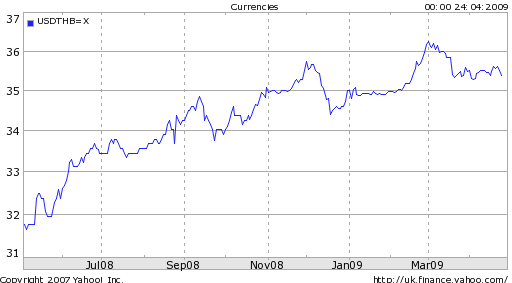




 Given the abysmal economic situation, it is no surprise that inflation has moderated. Commodity prices are well below the record highs of 2008. Aggregate demand, and GDP by extension, are retreating in kind. According to one economist, ” ‘
Given the abysmal economic situation, it is no surprise that inflation has moderated. Commodity prices are well below the record highs of 2008. Aggregate demand, and GDP by extension, are retreating in kind. According to one economist, ” ‘
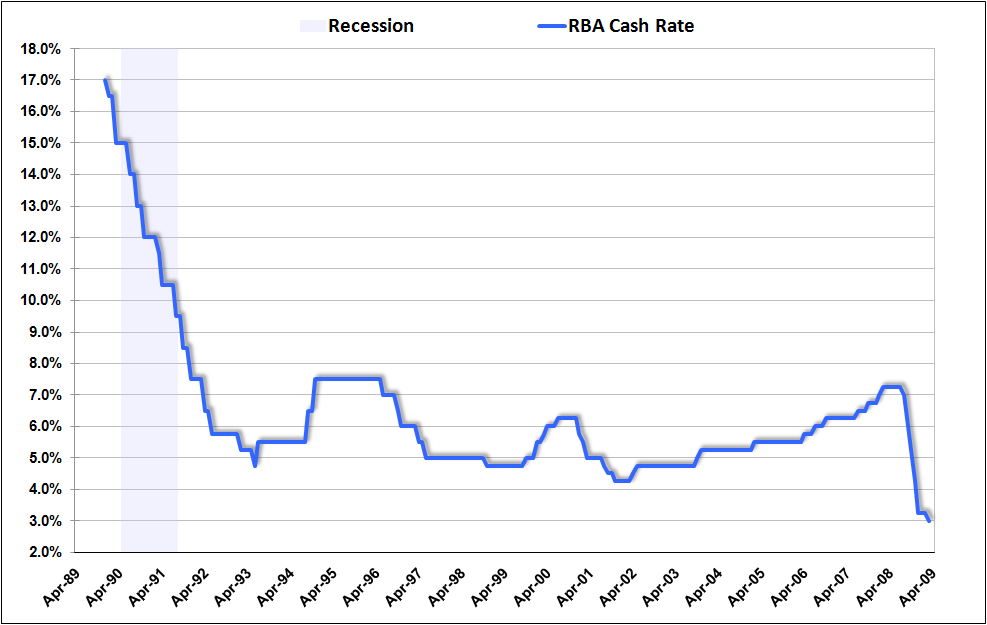
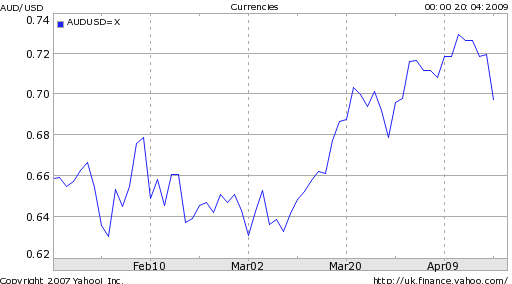
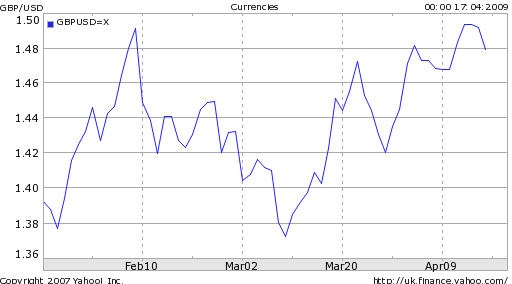
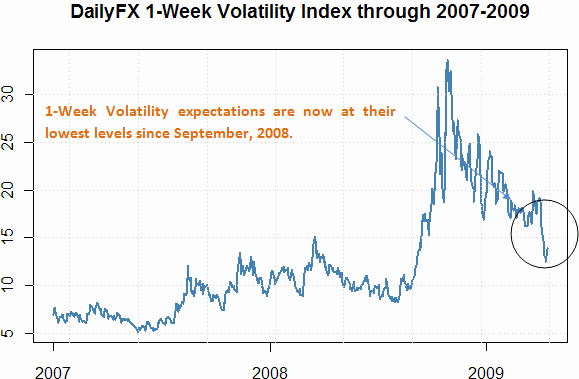
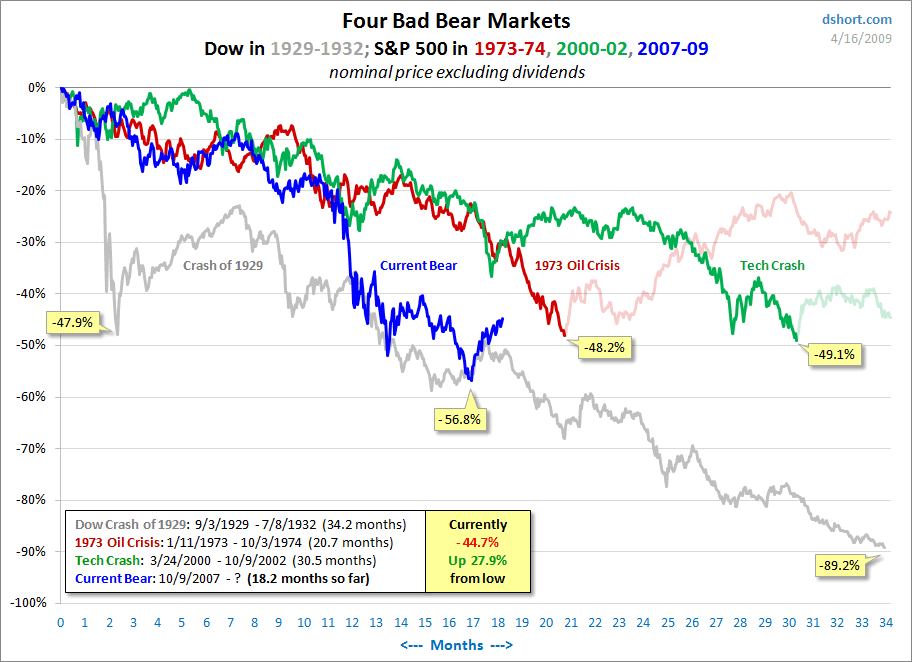 The difficulty with forecasting the current recession is that its causes are structural rather than cyclical. Argues one analyst: “It is unwise and foolish to treat this bear market like any other in the post-WW II period because it is totally unique; the scope and depth of the ongoing destruction of consumer and business credit, bank balance sheet compression and insolvency, consumer retrenchment and soaring unemployment should not be underestimated.” As a result, many economic models are out of date. “Economic forecasters have underestimated how bad it is because they have over-estimated the strength of the real economy and failed to take into account the extent of its dependence upon a buildup of debt that relied on asset price bubbles.”
The difficulty with forecasting the current recession is that its causes are structural rather than cyclical. Argues one analyst: “It is unwise and foolish to treat this bear market like any other in the post-WW II period because it is totally unique; the scope and depth of the ongoing destruction of consumer and business credit, bank balance sheet compression and insolvency, consumer retrenchment and soaring unemployment should not be underestimated.” As a result, many economic models are out of date. “Economic forecasters have underestimated how bad it is because they have over-estimated the strength of the real economy and failed to take into account the extent of its dependence upon a buildup of debt that relied on asset price bubbles.”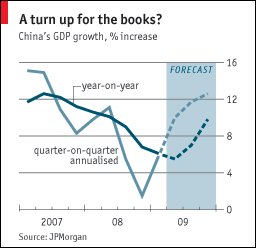
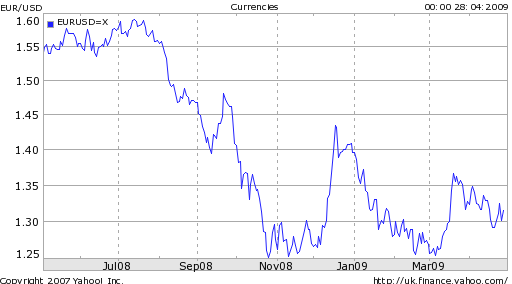
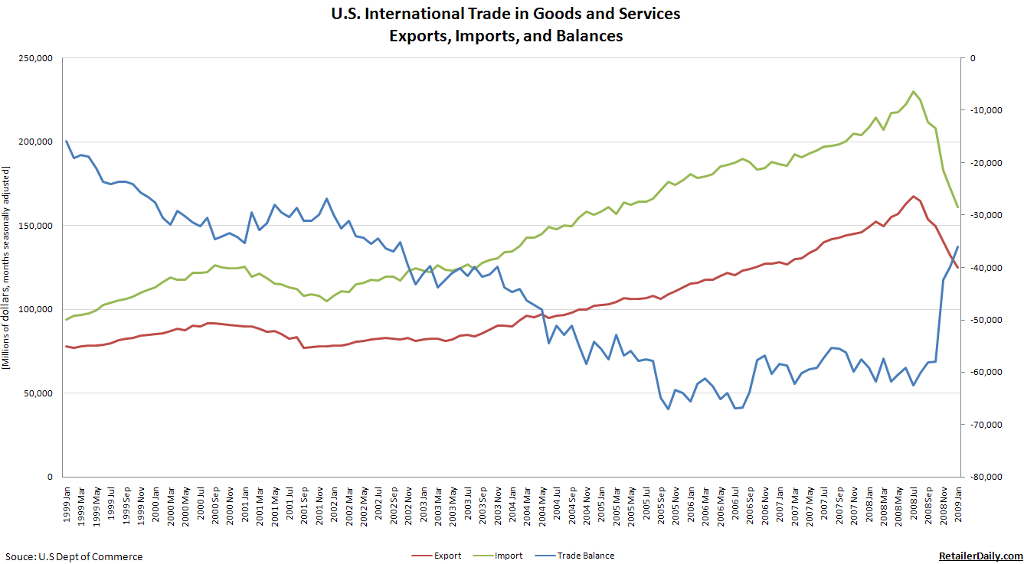 Ironically, an improvement in corporate profitability would further drive risk-taking and would thus have the effect of weakening the Dollar. One would think that an improved economic outlook would strengthen the Dollar. In actuality, financial and psychological factors continue to predominate in financial markets, and investors are looking for an excuse to dump the Dollar in favor of higher-yielding alternatives.
Ironically, an improvement in corporate profitability would further drive risk-taking and would thus have the effect of weakening the Dollar. One would think that an improved economic outlook would strengthen the Dollar. In actuality, financial and psychological factors continue to predominate in financial markets, and investors are looking for an excuse to dump the Dollar in favor of higher-yielding alternatives.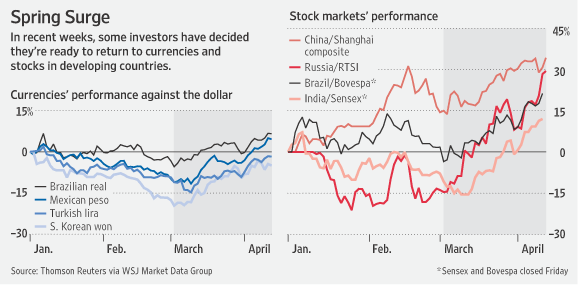
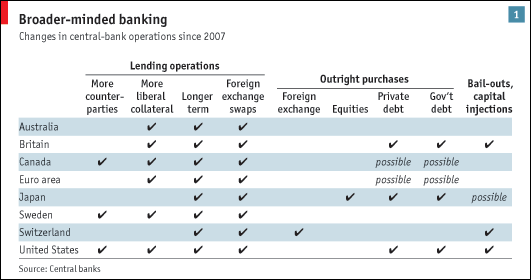
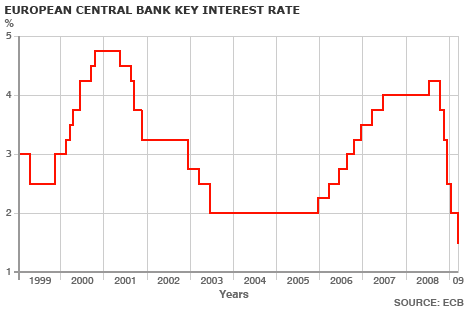 There are a few explanations. First of all, it’s possible that the ECB is selectively interpreting data as a basis for deriving a more optimistic economic forecast. Given the spate of recent bad news emanating from Europe, however, this seems unlikely. Besides, no less than Trichet himself has suggested that an economic recovery is
There are a few explanations. First of all, it’s possible that the ECB is selectively interpreting data as a basis for deriving a more optimistic economic forecast. Given the spate of recent bad news emanating from Europe, however, this seems unlikely. Besides, no less than Trichet himself has suggested that an economic recovery is