June 20th 2011
Japanese Yen In “No Man’s Land”
This, according to a hedge fund manager that has decided to cancel all of his fund’s bearish bets on the Japanese Yen. The reason: the yen is rising, and it’s unclear when – or even if – the government will intervene to push it back down. Even though the yen’s strength is fundamentally illogical, it seems that investors are growing increasingly wary of betting against it.
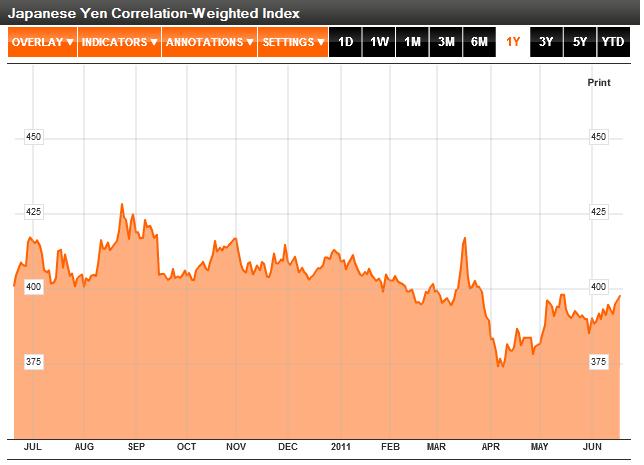
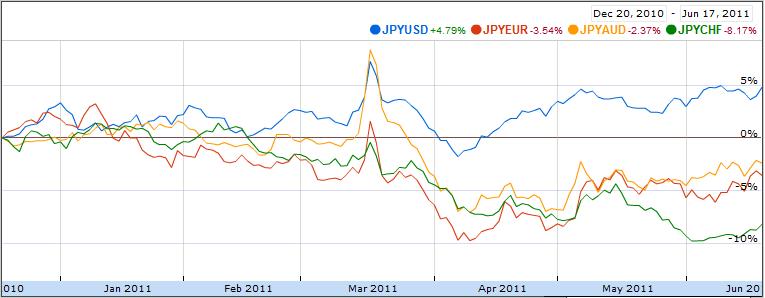
As I pointed out in my previous post on the Yen (“Japanese Yen Strength is Illogical, but Does it Matter?“), the yen has actually fallen over the last twelve months, on a correlation weighted basis (though to be fair, it has staged a pretty impressive comeback since the beginning of April). Unfortunately, investors mainly care about how it is performing against a handful of key currencies, namely the US Dollar. Simply, the yen continues to rise against the dollar, and it is unclear when it will stop.
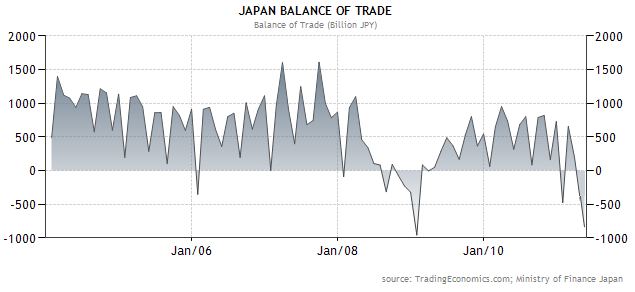
Japanese government analysis has indeed confirmed that “speculators” are behind the strong yen, as the alleged wide-scale repatriation of yen by Japanese insurance companies has yet to materialize. Of course, there isn’t really much doubt: Japan’s economy is contracting, due to decrease in output spurred by the tsunami. In May, it recorded its second largest monthly trade deficit ever.
Meanwhile, interest rates and bond yields are pathetically low, and the Bank of Japan is being urged to expand its asset buying program, which would theoretically result in a devaluation of the yen. As a result, retail Japanese forex traders (nicknamed “Mrs. Watanabes“) have resumed shorting the Yen as part of a carry trade strategy.
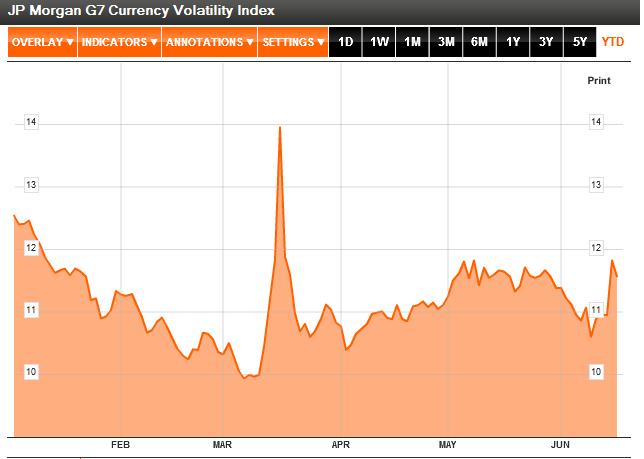
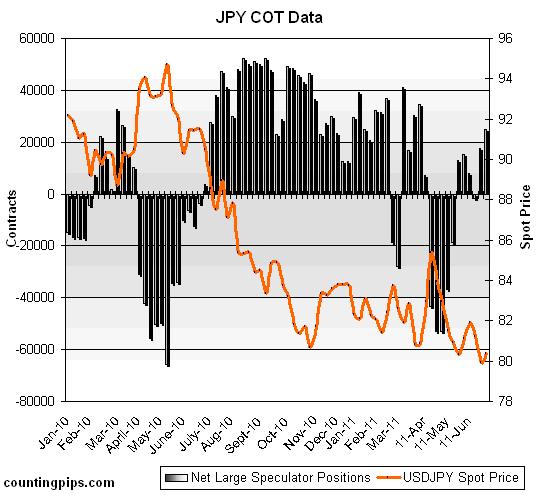
Alas, speculators either don’t share their pessimism or are running out of patience. While everyone continues to assume that the BOJ will intervene if the Yen rises to 80 against the dollar, no one can be sure whether the line in the sand might not be 78 or even 75. At this point, intervention seems to hinge more on politics than on economics, which means predicting it is beyond the scope of this post. In other words, “There is too much uncertainty and volatility in markets right now to make that yen trade appealing.” And sure enough, the most recent Commitments of Traders data shows that speculators have been re-building their yen long positions over the last month.
In the end, the speculators are probably right. The Bank of Japan has intervened twice over the last twelve months, and the impact has always been short-lived. Besides, given that many speculators still remain committed to shorting the yen, it remains extraordinarily vulnerable to the kind of short squeeze that sent it soaring 5% in a single session en route to the record high it touched in March.
I’m personally still bearish on the yen, but I also think it’s too risky to short it against the dollar, which seems to be declining for its own reasons. As you can see from the chart below, the yen has fallen against virtually every other major currency. Yen shorters, then, might be wise to avoid the dollar altogether and focus instead on any number of other currencies.