March 13th 2009
Central Banks Maintain Holdings of US Treasury Securities, but For How Long?
Yesterday, Chinese Premier Wen Jiabao aired his country’s growing concerns about continuing to lend money to the US. Within the context of the US economic stimulus plan and other related US spending initiatives, Mr. Wen is understandably anxious about China’s vast holdings of US Treasury securities:
President Obama and his new government have adopted a series of measures to deal with the financial crisis. We have expectations as to the effects of these measures. We have lent a huge amount of money to the U.S. Of course we are concerned about the safety of our assets. To be honest, I am definitely a little worried.
While the announcement represented political posturing (to an increasingly restless, domestic Chinese audience), it should nonetheless be heeded as a warning, that the US cannot expect China (and other foreign Central Banks) to fund US budget deficits indefinitely.
Let’s put aside the rhetoric for a moment, and examine the data. This week witnessed strong demand for Treasury securities, which were auctioned by the Treasury Department on consecutive days. Despite historically low yields (see chart), investors continue to snap up Treasury Bonds, mainly for the sake of risk aversion. The newly-revived issuance of 30-year bonds also went off without a hitch, and were more than 2x oversubscribed. Most relevant to this discussion is the fact the foreign Central Banks accounted for as much as 46% of demand!
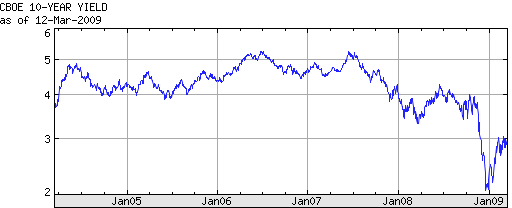
The most recent Federal Reserve Statistical Release paints a similar picture. While foreign Central Banks and other international institutions reduced their holdings of US government securities slightly from the previous week, the decrease was essentially negligible. Overall, such entities have increased their holdings by at least $440 Billion over the previous year, bringing the total to approximately $3 Trillion (depending on the data source). China’s contribution remains substantial. Of its $2 Trillion in foreign exchange reserves, “Economists say half of that money has been invested in United States Treasury notes and other government-backed debt.”
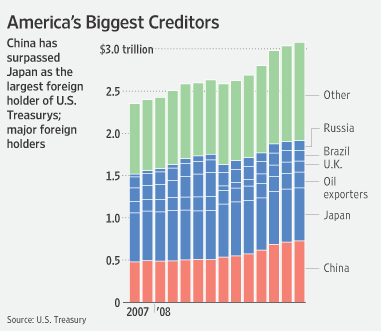
However, there are a few reasons why I don’t think this trend will continue. First of all, the buildup in foreign Treasury holdings that transpired over the last decade was largely a product of unsustainable global economic imbalances, as net exporters to the US invested their perennial trade surpluses in what they perceived to be the world’s most secure investment. Temporarily putting aside whether Treasuries are actually secure, economic indicators suggest that Central Banks simply do not have the capacity to increase their holdings by much more. China’s trade surplus plummeted to $4.8 Billion last month; one economist projects a surplus of only $155 Billion in 2009, compared to nearly $300 Billion in 2008.
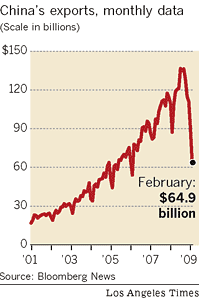
You can also remove from the list Japan- the second-largest holder of US Treasury securities- which is now running a trade deficit. Instead, both countries have publicly announced plans to use some of their forex reserves to fund domestic economic initiatives.
Then there is the equally unsustainable short-term buildup in US Treasuries, which is largely a product of technical factors. As I mentioned above- and which should be clear to all investors- the current theme underlying securities markets is one of risk aversion. In fact, it now appears that a bubble is forming in the bond market, and “any exodus now could spark selling across the board. Foreign debt holders would likely repatriate their funds immediately to reduce the risk of being last to convert.” As soon as markets recover- of which there are already nascent indications– investors will probably reduce their holdings of government bonds, or at least not increase their holdings.
Even the most conservative projections indicate a cumulative budget deficit for the next few years measuring in the the Trillions. Unless the risk-aversion theme obtains for the next decade, it seems unlikely that foreigners can be tapped to fund more than a small portion, leaving the Federal Reserve (with the help of its printing press) to make up the shortfall.



March 14th, 2009 at 8:03 am
[…] Forex blog on China being nervous about US treasuries. It helps understand the dangers for the US dollar coming from China. […]
March 14th, 2009 at 9:36 am
China should be worried about their dangerous over investment in US Treasury obligations. Washington ’s long-term choice is either repudiation or monetization. For monetization to be effective, the depreciation in the dollar would have to be substantial and this in turn would dramatically raise prices of imports for American consumers which would mean a tremendous drop in foreign imports. Debt monetization would cause more disruption to exporting nations than selective repudiation of Treasury debt.
Washington has bailed out the banks, Wall Street & their Washington special interests and much of the cost is added to the national debt to by paid by this and future generations while real estate and investments continue to fall. Find out what a growing repudiate the debt movement could mean for treasury bonds, the dollar, gold and the stock market.
The Campaign to Cancel the Washington National Debt By 12/22/2013 Constitutional Amendment is starting now in the U.S. See: http://www.facebook.com/group.php?gid=67594690498&ref=ts
Thanks, Ron
March 16th, 2009 at 12:14 pm
China knows that they are stuck in the middle. No matter how big China’s economy is, the main global economic engine is still Uncle Sam. It is in the best interest of the economic powers that Uncle Sam is alive and kicking. Look how the subprime crisis affected the rest of the world.
March 18th, 2009 at 8:04 pm
[…] Chinese warned the US against printing too much currency. But the US federal government deficit could easily hit 2 […]
March 23rd, 2009 at 11:21 am
[…] Chinese Premier Wen Jiabao (as the ForexBlog reported here) expressed doubts about China’s US loans and investments two weeks ago, the markets have been […]