August 26th 2010
“Risk-On, Risk-Off”
It sounds like a play on words, based on the Karate Kid refrain, Wax-On Wax Off, and for all I know it was. Still, I rather like this characterization – coined by a research team at HSBC – of the markets‘ current performance. Moreover, you’ll notice from the placement of that apostrophe that I’m not just talking about forex markets, but about the financial markets in general.
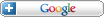
What we mean is that when risk appetite is high, credit markets and equities and high-yielding currencies tend to rally together. When risk appetite fades, “those assets fall and government bonds and safe-haven currencies, including the U.S. dollar, the Swiss franc and, in particular, the Japanese yen rally.” Data from Bloomberg News confirms this phenomenon: “The 120-day negative correlation between Intercontinental Exchange Inc.’s Dollar Index and the Standard & Poor’s 500 Index was at 42.4 percent today, and has been mostly above 40 percent since June 2009.”
Skeptics counter that this correlation is tautological. Anyone can point to a stock market rally and declare that “Risk is Back On.” In addition, it’s not wholly unsurprising that there are strong correlations between low-risk currencies and low-risk assets, and between high-risk currencies and high-risk assets. According to HSBC, however, this time is different.
For example, models suggest that the recent decline in volatility should have caused these relationships to break down. That they defied predictions and remained strong suggests that we have witnessed a significant paradigm shift. In the past, “Rising correlations are also tied to weak macroeconomic conditions.” At the moment, this could hardly be more true, with global economic growth flagging.
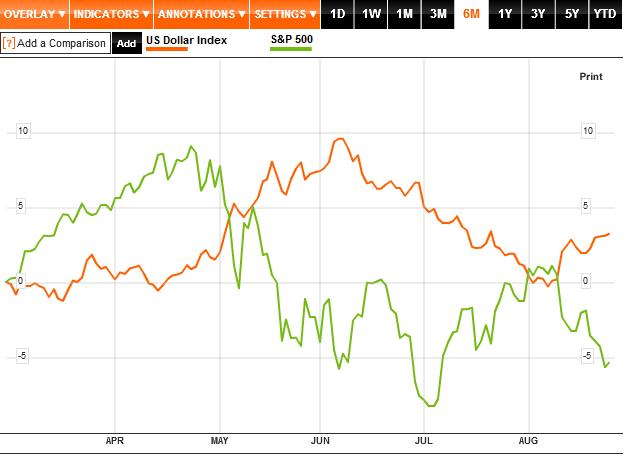
Statisticians love to teach the dictum, Correlation does not imply causation. Nonetheless, I think that in this case, I’d wager to say that the equity and credit/bond markets are driving forex, rather than the other way around. Consider as evidence that, “[Retail] Investors withdrew a staggering $33.12 billion from domestic stock market mutual funds in the first seven months of this year,” and shifted this capital into bonds. While this wouldn’t in itself be enough to drive the Dollar higher, it epitomizes the steady shifts that have been taking place in capital markets for nearly a year, broken only by the S&P/Euro rally in the spring (which now appears to have been an aberration).
In fact, these shifts are once again creating shortages of Dollars: “This week, two banks bid at the European Central Bank’s weekly dollar liquidity providing auction – the first time there have been any bids since May – suggesting that they could not raise dollars in the market.” This suggests that demand for the Dollar could continue to grow.
Some analysts have suggested that the low-yielding US Dollar is already on its way to becoming a funding currency for carry traders, but I think this is wishful thinking. The HSBC report supports this conclusion, “A weakening of the ‘risk on-risk off’ paradigm is likely only once macro conditions are improved in a sustainable way…Currency performance will likely be tied to the ebb and flow of the perception of risk for some months to come.” In short, until there is solid proof that the global economy has emerged from recession (even if ironically it is the US which is leading the pack downward), the Dollar will probably remain strong.